The Pros and Cons of Solid-State Drives (SSDs) vs. Traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
Speed and Performance
One of the most significant advantages of SSDs over HDDs is their speed and performance. SSDs use flash memory to store data, which allows for much faster read and write speeds compared to HDDs. This means that when you boot your computer or open a program, it will happen almost instantly with an SSD.
In contrast, HDDs rely on spinning platters to access data, which can lead to longer load times and slower performance. The speed difference between SSDs and HDDs is especially noticeable in high-performance applications such as gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering. These tasks require fast data transfer rates and seek times, which SSDs provide much better than HDDs.
However, the speed advantage of SSDs comes at a cost. High-speed SSDs are more expensive per gigabyte compared to HDDs. This means that for users who need large amounts of storage space on a tight budget, an HDD may be a more cost-effective option despite its slower performance.
Durability and Reliability
Another significant difference between SSDs and HDDs is their durability and reliability. SSDs have no moving parts, which makes them less susceptible to physical damage from drops or vibrations compared to HDDs. This is especially important for users who frequently travel with laptops or use external drives in rugged environments.
Additionally, SSDs are generally more reliable than HDDs due to their lack of mechanical components that can fail over time. HDDs have several moving parts, including the read/write head and platters, which can wear out or become misaligned, leading to data loss or drive failure. SSDs also tend to last longer in terms of write cycles before wearing out.
However, SSDs are not invincible. They still have a limited lifespan due to their flash memory’s finite number of program/erase cycles. This means that heavy usage over time can lead to wear and tear on the drive’s cells, potentially causing data loss or drive failure. It is important for users to consider this when selecting an SSD for applications that require frequent writing or erasing.
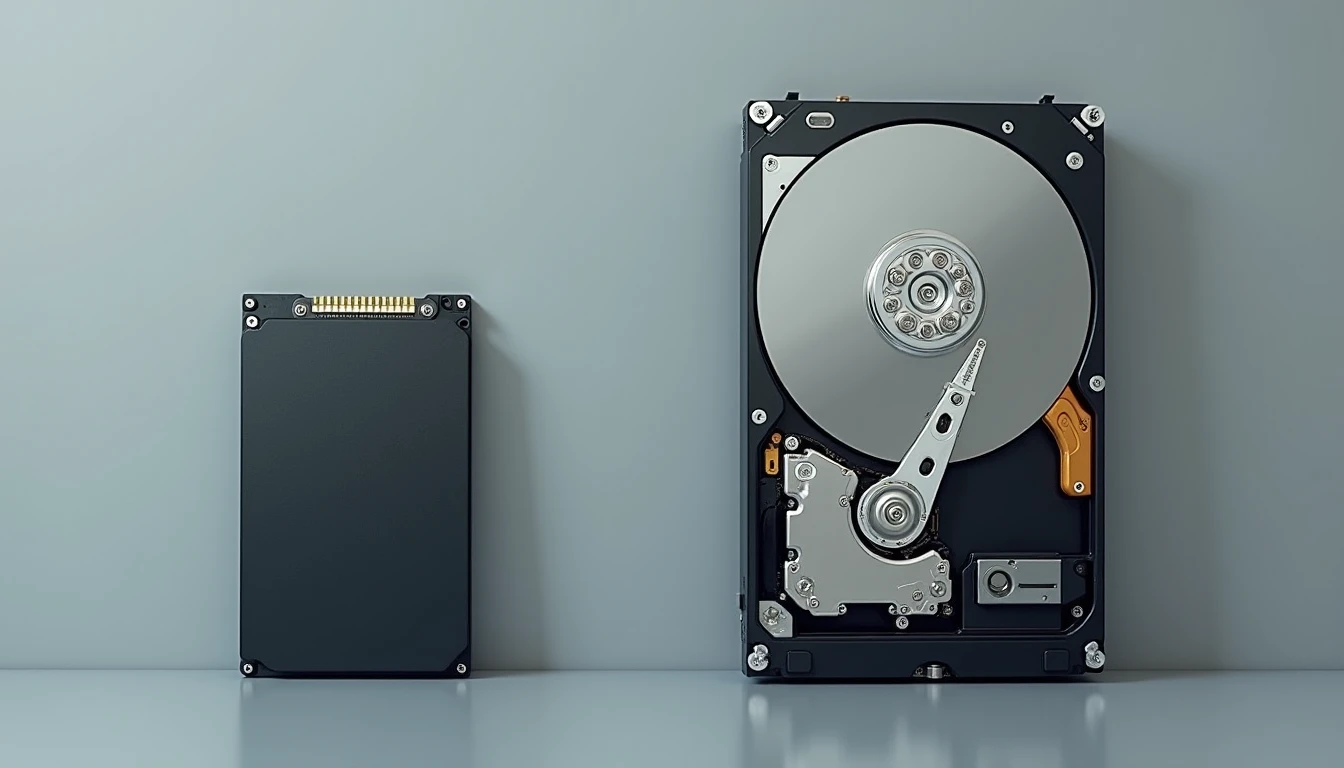
Power Consumption
Power consumption is another area where SSDs have a significant advantage over HDDs. Because SSDs do not have any moving parts, they consume less power than HDDs. This makes them ideal for use in laptops and other mobile devices where battery life is critical.
In addition to extending battery life, lower power consumption also means that SSDs generate less heat compared to HDDs. This can help improve system stability and reduce the need for active cooling solutions such as fans or liquid cooling systems.
However, it’s important to note that while SSDs consume less power overall, their power draw can fluctuate more than HDDs based on usage patterns. For example, when an SSD is being written to frequently, its power consumption may spike temporarily before returning to a lower idle state. This variability in power consumption should be taken into account when designing systems or selecting components.
Form Factor
Another key difference between SSDs and HDDs is their form factor. SSDs come in various sizes, including 2.5-inch drives for laptops and desktop computers, M.2 drives for smaller devices like ultrabooks and gaming PCs, and even PCIe cards for high-end servers and workstations.
This variety of form factors allows users to choose the best option for their specific needs and available space. For example, an M.2 SSD can be used in a thin laptop where a 2.5-inch drive would not fit, while a larger 3.5-inch HDD may be preferable for a desktop computer with plenty of room.
However, this flexibility also means that users need to consider compatibility when selecting an SSD or HDD. Not all devices support every form factor, and some may require additional adapters or mounting hardware. It’s important to carefully research your specific needs before making a purchase.
Cost
Cost is one of the most significant factors for many users when choosing between SSDs and HDDs. While prices have been coming down over time, SSDs are still more expensive per gigabyte than HDDs. This means that if you’re looking for large storage capacities on a tight budget, an HDD may be the better choice.
However, it’s important to consider the value proposition of an SSD despite its higher initial cost. While an HDD might offer more raw capacity for less money, an SSD can provide faster performance and potentially extend the life of your system components by reducing power consumption and heat generation. For many users, especially those who prioritize speed and reliability over maximum storage space, the benefits of an SSD outweigh its higher price tag.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that prices for both SSDs and HDDs are constantly changing due to market demand and technological advancements. It’s always a good idea to shop around and compare prices from multiple retailers before making a purchase.
In conclusion, when choosing between an SSD and an HDD, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Both have their own unique advantages and disadvantages that should be carefully considered based on your specific needs and budget. By weighing factors like speed, durability, power consumption, form factor, and cost, you can make the best decision for your individual requirements.
